- Businesses and Digital Transformation: Organizations are embracing digital transformation and adopting technology to enhance productivity, reduce expenses, and revolutionize the customer experience.
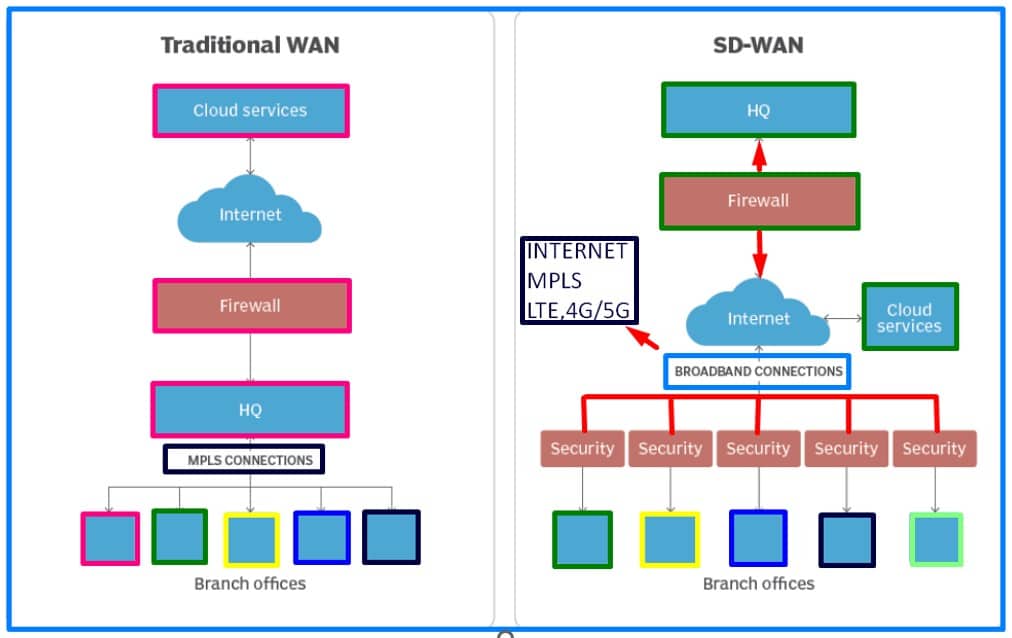
- Traditional WAN’s Role: The traditional function of the wide area network (WAN) was to connect branch or campus users to applications hosted on data center servers, employing dedicated MPLS circuits for secure and reliable connectivity.
- Challenges in a Digital World: In the digital age, applications are moving to the cloud, and users accessing them are increasingly mobile with diverse devices. This shift presents challenges for traditional WAN networks.
- Struggles with Business-Critical Applications: As businesses adopt SaaS and IaaS across multiple clouds, IT departments face difficulties in providing satisfactory experiences for critical applications.
- Inefficiencies of Traditional WANs: Traditional WANs heavily depend on data center infrastructure for cloud connectivity, resulting in higher latency, data center overload, and a single point of failure.
- Bandwidth Demands and Upgrades: The explosion of bandwidth demands puts immense strain on network capacity, leading to constant upgrades of private WAN circuits.
- Consideration of Internet Circuits: Some organizations explore commodity internet circuits with higher capacity and lower costs but encounter challenges in operationalizing them for business-critical connectivity, often relying on an inefficient active/standby approach.
- Security and Compliance Concerns: Exposing an enterprise to the internet raises threats and compliance issues, as it becomes challenging to protect critical assets accessed by a diverse workforce with varying access levels.
- SD-WAN’s Evolution: Software-defined wide-area networking (SD-WAN) solutions have evolved to tackle these challenges.
- SDN and Network Management: SD-WAN is part of the broader technology of software-defined networking (SDN), which centralizes network management by abstracting the underlying infrastructure from applications.
- Decoupling of Plane in SDN: SDN decouples the forwarding plane from the control and management plane, enabling centralized network intelligence, more automation, simplified operations, and efficient provisioning and troubleshooting.
- SD-WAN Application: SD-WAN applies SDN principles to the WAN, aiming to address the challenges faced by modern WAN requirements.
- SD-WAN as GPS for WAN: To explain SD-WAN’s benefits, consider the analogy of traveling by car. Just as GPS navigation transformed car travel, SD-WAN revolutionizes WAN architectures by providing centralized guidance for traffic forwarding.
- Dynamic Routing and Enhanced Efficiency: SD-WAN dynamically routes traffic based on real-time network conditions, enhancing efficiency and performance for critical applications.
- Centralized Management and Improved User Experience: SD-WAN offers centralized visibility and control, simplifying network management and enhancing the user experience.