Domain Identification(DID) : A domain ID which helps to make logical group of vedge routers and vsmart controllers in cisco SD-WAN. A vedge router can make connection with vsmart controllers in same domain. Domain ID should be unique. Now a days in cisco SD-WAN we can configure only one domain in an overlay network.
Overlay ID: Overlay ID is a unique identifier used to distinguish between different virtual networks or overlays that are created on top of the physical network infrastructure. It is used to segregate traffic of different applications or user groups within a larger SD-WAN network.
OMP: OMP: Overlay Management Protocol (OMP) is a cisco propriety protocol, which helps to establish and maintain the SD-WAN control plane traffic. The default admin distance value is 250. It runs between the controllers as well as between vedge routers and vsmart controllers. We can compare it as BGP peering between a route-reflector and an RR client established between loopback interfaces.OMP redistributes Static, Connected and OSPF(IA) routes automatically but BGP needs to redistribute manulaly
The System-IPs are used to form OMP peering, one WAN Edge router and one vSmart controller make one connection even if there would be several DTLS connections on same controller. It distributes TLOCs, Service-Chaining, Service-side information, data plane security parameters, VPN labels, and crypto keys, data and application-aware routing (AAR) policies.
We can see in below screenshot where only one OMP peering is formed between wan edge router and vsmart controller despite it has two or more transport.
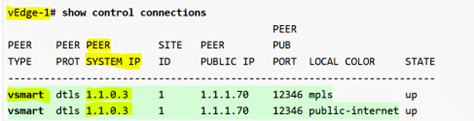
However, if we check how many OMP peering sessions to the controller there are, we can see that there is only one.
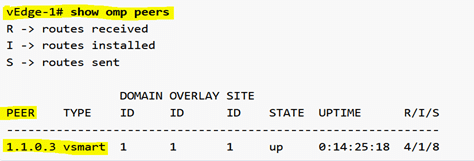
Pic: One OMP Peering
Site ID: A site is a particular physical location within the Cisco SD-WAN overlay network, such as a branch office, a data center, or a campus. It is 32 bit number. The site-id plays a similar role to a BGP AS number. It is primarily used for loop prevention. All sites should have a unique site ID, and all devices at the same location should have the same site-id. Site id use to create policy. As like ACL we use site-list to identify edges to apply policy.
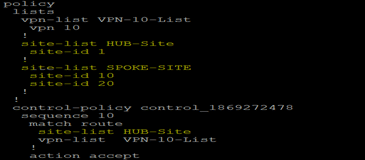
Pic: Site-list uses in policy creation
System IP Address: This address is like the router ID on a regular router. The system IP address provides permanent network overlay addresses for vEdge routers and vSmart controllers. It should be unique throughout the overlay fabric. It is 32 bit number. We can write the system IP address as we would an IPv4 address, in decimal four-part dotted notation. System-id 10.255.255.1. The OMP peering uses the System-Ips to establish peer between vsmart and vedge.
OMP Routes: Prefixes that live in our service side VPN. These prefixes can be injected into OMP as either Connected, Static routes or redistributed in from BGP or OSPF running in the service side VPN. OMP routes require and resolve into TLOCs for functional forwarding. In comparison with BGP, an OMP route is the equivalent of a prefix carried in any of the BGP AFI/SAFI field.
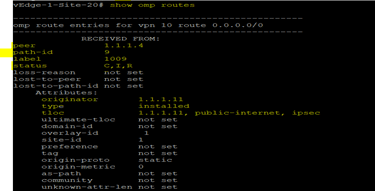
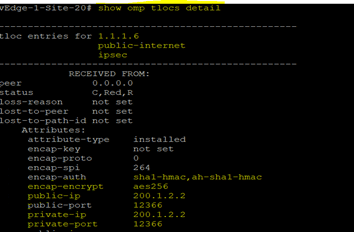
TLOC : A TLOC, or transport location, identifies the physical interface where a vEdge router connects to the WAN transport network or to a NAT gateway. It uses three tuple system ip,color, encapsulation. In this tuple, IP address is the system IP address and color is a fixed text string that identifies transport whether public or private network, by default encapsulation uses IPsec. OMP advertised TLOCs using TLOC routes.
TLOC: (System IP, Color- Public, Private, Mpls etc, Encapsulation Type-IPsec/GRE)
TLOC Color: TLOC Color is a logical abstraction used to identify specific WAN transport that connects to a WAN Edge device. The color is a statically defined keyword that distinguishes a particular WAN transport as either public or private and is globally significant across the Cisco SD-WAN fabric.
TLOC Routes: advertise Transport Locators of the connected WAN transports, along with additional attributes such as public and private IP addresses, color, TLOC preference, site ID, weight, tags, and encryption keys.
Service routes: advertise embedded network services such as firewalls and IPS that are connected to the vEdge local-site network.
Service ID: The service-id defines the type of service that is being advertised. There are 7 pre-defines values:
- FW maps to svc-id 1;
- IDS maps to svc-id 2;
- IDP maps to svc-id 3;
- Custom Services: The last four values are used for customer defined services:
- netsvc1 maps to svc-id 4;
- netsvc2 maps to svc-id 5;
- netsvc3 maps to svc-id 6;
- netsvc4 maps to svc-id 7;
Network Management System (NMS): The vManage NMS is a centralized network management system that lets you configure and manage the entire overlay network from a simple graphical dashboard. providing a centralized view of network status, performance, and configuration information, and enabling administrators to manage and troubleshoot the network efficiently and effectively.
BFD: The BFD (Bidirectional Forwarding Detection) is a protocol that detects link failures as part of the Cisco SD-WAN (Viptela) high availability solution, is enabled by default on all vEdge routers, and you cannot disable it. BFD session will form between the sites not within the sites.
